In Visum, several assignment procedures are structured as follows: First, a number of alternatives (routes or connections) is determined. Then the total demand per OD pair is distributed across these alternatives. These are the (static) stochastic PrT assignment, the dynamic-stochastic PrT assignment and the timetable-based PuT assignment. PrT assignment procedures use alternative routes from origin zone to destination zone, whereas the PuT assignment procedure provides alternative connections (routes with detailed departure times). For simplification, we will only mention routes below in this section.
A distribution model determines the share of demand which is assigned to a certain route. This portion depends on the impedance of a route. In all cases, percentage Pia, of route i, is determined based on the demand of an OD pair within time interval a, so that impedance Ria is applied in a distribution function, allowing the program to calculate utility Uia of the route. For this distribution function the Kirchhoff, Logit, Box-Cox, Lohse models and Lohse with variable Beta are available. The following approach applies to all models:
1. Impedance Ria is converted to the utility Uia of route i in the time interval a:
Uia = f(Ria)
2. From this utility Uia the percentage of demand Pia is calculated (where n is the total number of routes).
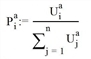
The models reveal differences in the functional relation f of impedance and utility.

